Migrate to Canada
Migrate to Canada Today!
Canada has long been a preferred destination for immigrants due to several key factors. Economic opportunities are among the most significant reasons people choose to migrate to Canada.
With a stable economy, a strong labour market, and a demand for skilled workers, many individuals seek to build careers in industries ranging from technology to healthcare.
Additionally, Canada offers a high quality of life, often ranking among the best countries in global quality of life indices. The country is known for its diversity and inclusiveness, making it an attractive option for people from all cultural backgrounds.
Another major draw is Canada's universal healthcare system, which ensures residents have access to essential medical services without the burden of large expenses.
The education system is also highly regarded, with excellent public schools, top-tier universities, and numerous pathways for international students to transition into the workforce and permanent residency.
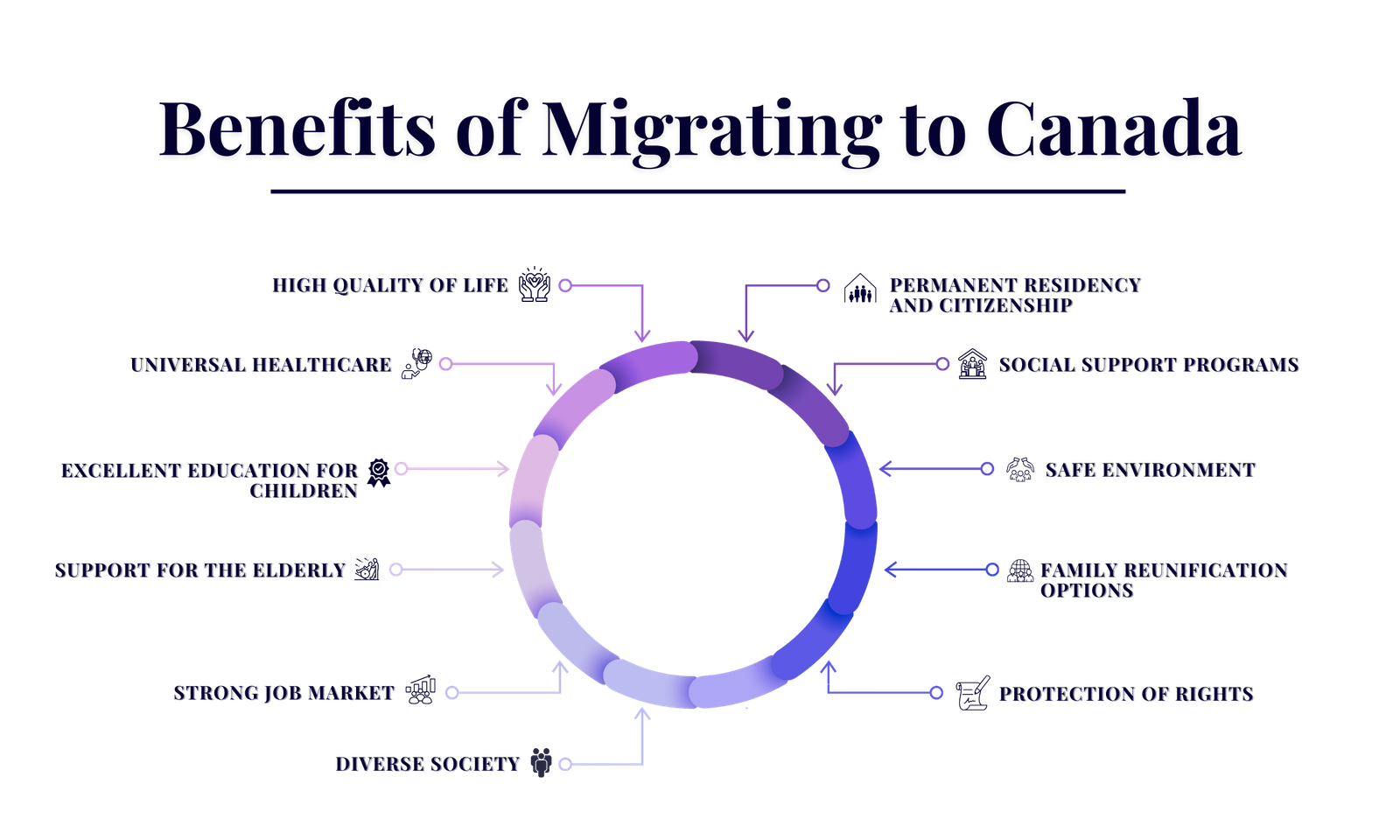
Benefits of Migrating to Canada
High Quality of Life
Canada is known for its excellent living conditions, with clean environments, low crime rates, and a good standard of living. Residents have access to many services and amenities such as:
Universal Healthcare
Canada provides government-funded healthcare, meaning all residents can access necessary medical services without worrying about high costs.
Excellent Education for Children
Canada has a strong education system that includes high-quality public schools and universities. Education is free for children from kindergarten through grade 12, ensuring that all kids have access to learning. Additionally, there are many programs and support services for international students who wish to continue their education in Canada.
Support for the Elderly
Canada offers various support programs for seniors, including pensions, healthcare services, and community support initiatives. These programs aim to ensure that elderly citizens have a good quality of life and access to necessary services as they age.
Strong Job Market
Canada’s economy is stable and growing, offering many job opportunities in various fields like technology, healthcare, and construction. The country actively seeks skilled workers to fill job vacancies.
Diverse Society
Canada is welcoming and multicultural, with people from many different backgrounds. This diversity helps newcomers feel accepted and find communities that reflect their culture.
Permanent Residency and Citizenship
Migrants can apply for permanent residency, which gives them many of the same rights as citizens. After living in Canada for a certain period, they can apply for Canadian citizenship.
Social Support Programs
Canada has various social support programs, such as unemployment benefits and pensions, which provide financial help when needed.
Safe Environment
Canada is politically stable and has low crime rates, making it a safe place to live and raise a family.
Family Reunification Options
Canada values family connections and offers programs that allow immigrants to sponsor their family members to come and live in Canada.
Protection of Rights
Canada strongly supports human rights and personal freedoms, ensuring everyone is treated equally and fairly under the law.
These benefits make Canada an appealing choice for those looking to improve their quality of life, find good jobs, and live in a welcoming environment, with excellent support for children and the elderly.
Types of Canadian Immigration Programs
1. Express Entry System
The Express Entry System is Canada’s primary immigration pathway for skilled workers.
Launched in 2015, it operates as an online points-based system designed to streamline applications for permanent residency under three key programs:
- Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSW): This program targets skilled professionals with foreign work experience and education, evaluating candidates based on criteria such as language proficiency, education, and work experience.
- Federal Skilled Trades Program (FST): This stream is for skilled tradespeople in fields such as construction, electrical work, and manufacturing. Candidates need job offers from Canadian employers or certification in their trade from a Canadian authority.
- Canadian Experience Class (CEC): This program is for temporary foreign workers or international graduates with Canadian work experience. It is an ideal pathway for those already living in Canada and seeking permanent residency.
Candidates in the Express Entry pool are ranked using the Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS). Those with the highest scores receive an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residency.
2. Provincial Nominee Programs (PNP)
The Provincial Nominee Program (PNP) allows individual provinces and territories to nominate candidates for permanent residency based on their unique labour market needs.
Each province has its own specific criteria and streams, which can focus on skilled workers, businesspeople, or students who wish to remain in that province.
For example, Ontario might focus on tech workers, while Alberta might prioritise those in agriculture or energy. The PNP serves as a way for regions to address local economic demands and population growth outside the federal system.
If nominated through a PNP stream aligned with Express Entry, candidates receive 600 additional points toward their CRS score, almost guaranteeing an ITA.
3. Quebec Immigration
Quebec has its own unique immigration system, separate from the federal programs, due to its distinct culture and the importance of the French language.
The primary immigration pathway in Quebec is the Quebec Skilled Worker Program (QSWP), which selects candidates based on factors like French language proficiency, education, and work experience.
Quebec's immigration process is largely autonomous, and applicants must receive a Certificat de sélection du Québec (CSQ) before they can apply for permanent residency through the federal government.
Quebec also offers programs for business immigrants and family sponsorships, but all applications are processed through its provincial system.
4. Family Sponsorship
Canada places a strong emphasis on family reunification. Through the Family Sponsorship Program, Canadian citizens and permanent residents can sponsor their close relatives to come and live in Canada. Eligible family members include:
- Spouses or common-law partners
- Dependent children
- Parents and grandparents
The sponsor must meet certain income requirements to ensure they can financially support their family members. Once approved, sponsored family members can live, work, and study in Canada as permanent residents.
5. Temporary Residence Pathways
Many immigrants come to Canada temporarily and transition to permanent residency later through various programs. The main temporary residence pathways include:
- Work Permits and the Temporary Foreign Worker Program (TFWP): This program allows foreign nationals to work in Canada for a specified period. Employers must often demonstrate that no Canadian workers are available for the job by obtaining a Labour Market Impact Assessment (LMIA).
- Study Permits and Post-Graduation Work Permits (PGWP): Canada is a popular destination for international students. Study permits allow students to pursue educational programs in Canada, and after graduation, they can apply for a Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP) to gain Canadian work experience. This work experience often serves as a pathway to permanent residency through programs like the Canadian Experience Class (CEC).
6. Business Immigration
Canada offers several immigration pathways tailored to entrepreneurs, investors, and self-employed individuals who wish to contribute to the economy through business ventures.
- Start-up Visa Program: This program is designed for entrepreneurs who have the support of designated Canadian organizations such as venture capital firms or angel investors. It encourages innovation and job creation.
- Self-Employed Program: This pathway targets individuals with relevant experience in cultural, artistic, or athletic activities, allowing them to immigrate to Canada as self-employed individuals.
- Investor and Entrepreneur Programs: While many provinces used to offer investor programs, these have become less common. However, some provinces still maintain programs for business owners and entrepreneurs willing to invest in the local economy.
A Deep Dive into Canada’s Points System: The Path to Becoming a Permanent Resident
Canada's immigration system uses a points-based approach to assess candidates applying through certain pathways, especially the Express Entry system.
This system assigns points based on several criteria to rank candidates, ensuring that the country selects immigrants with skills that contribute to the economy.
The Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) is the scoring method within Express Entry, where individuals with the highest scores receive an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residency.
Points Systems in Other Immigration Programs
Besides Express Entry, other programs may have their own points-based evaluations. For example, many provinces operate their own Provincial Nominee Programs (PNP), which use province-specific criteria to assess applicants. Quebec also has its own system for selecting immigrants, separate from the federal process.
Factors That Influence the Points System
Several core factors determine the number of points candidates receive:
1. Age
Younger applicants are given more points, particularly those between the ages of 20 and 29. As applicants grow older, the points awarded for age gradually decrease, with no points allocated for individuals over 45.
2. Education
Higher educational achievements result in more points. Applicants with qualifications such as a master’s or a Ph.D. earn a significant number of points.
However, those who obtained their education outside of Canada must have their degrees verified through an Educational Credential Assessment (ECA) to ensure they are equivalent to Canadian standards.
3. Language Proficiency
Proficiency in one or both of Canada’s official languages—English and French—earns candidates valuable points. Applicants must take approved language tests, such as the IELTS or CELPIP for English, and the TEF for French.
Points are awarded for each section of the test: listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Candidates fluent in both languages can also gain additional points.
4. Work Experience
Work experience, both in Canada and abroad, plays an important role. Applicants can earn points based on the number of years they’ve worked in skilled occupations, particularly those classified under Canada’s National Occupational Classification (NOC) system.
Candidates who have gained experience working in Canada will receive extra points.
5. Job Offer
A valid job offer from a Canadian employer can significantly boost an applicant’s score. Higher points are awarded for skilled job offers that are supported by a Labour Market Impact Assessment (LMIA), which confirms the employer's need to hire a foreign worker.
6. Provincial Nomination
If a candidate is nominated by a Canadian province or territory through the Provincial Nominee Program (PNP), they are granted an additional 600 points, which essentially guarantees an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residence.
7. Adaptability
Canada values candidates who are likely to settle successfully. Points are available for factors that suggest the applicant will integrate well, such as having a spouse with language proficiency, previous work or study experience in Canada, or family members already living in the country.
Breakdown of Points
Under the Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS), candidates can earn a maximum of 1,200 points. This is broken down as follows:
- Core Factors: Age, education, work experience, and language proficiency can add up to 600 points.
- Additional Factors: Factors like a provincial nomination, a job offer, or having Canadian education can contribute up to another 600 points.
Example of Points Allocation:
- Age: Candidates aged 20-29 can earn up to 110 points.
- Language Proficiency: High scores in language tests can yield up to 136 points for proficiency in the first official language, with additional points for the second.
- Education: A Ph.D. or equivalent earns up to 150 points.
- Work Experience: Applicants with five or more years of work experience can earn up to 80 points, with added points for Canadian work experience.
CRS Cut-Off Scores and Invitations to Apply (ITA)
Every few weeks, Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) conducts Express Entry draws, inviting top-ranking candidates to apply for permanent residency.
The minimum CRS score required to receive an ITA varies based on each draw, influenced by the pool of applicants at that time. Recent cut-off scores often provide insight into the score range needed to secure an invitation.
How to Improve CRS Scores
Candidates can take various steps to increase their CRS scores and improve their chances of receiving an ITA:
- Improve Language Scores: Retaking language tests to achieve higher scores can significantly boost the overall score.
- Further Education: Earning an additional credential, such as a diploma or degree, can increase points under the education factor.
- Provincial Nomination: Applying for a provincial nomination can immediately add 600 points to the candidate’s total.
- Canadian Work Experience: Securing a temporary work permit to gain Canadian work experience can increase points.
- Job Offer: Finding a job in Canada that meets LMIA requirements also helps to increase points.
Canada’s immigration landscape presents a variety of pathways for individuals and families eager to explore new opportunities. At Cross Border, we take pride in our proven track-record of assisting clients in navigating this intricate system, helping them realise their aspirations of settling in Canada.
Our comprehensive experience with various immigration programs—such as the Express Entry System, Provincial Nominee Programs, and family sponsorship—has allowed us to support 1300+ individuals in successfully obtaining permanent residency.
Frequently Asked Questions
The official website of the Government of Canada does not provide an age restriction for applying for Canadian permanent residency. However, an age limit is defined broadly. This is because, beyond a certain age, candidates find it more difficult to achieve the criterion for 67 points. This is because they will not receive any points based on their age.
FSWP basic eligibility requires 67 points out of 100. Those who score less than 67 do not qualify.
Yes, IELTS is required to migrate to Canada and in order to get a Canadian visa; one must prove their language proficiency to the IRCC.



